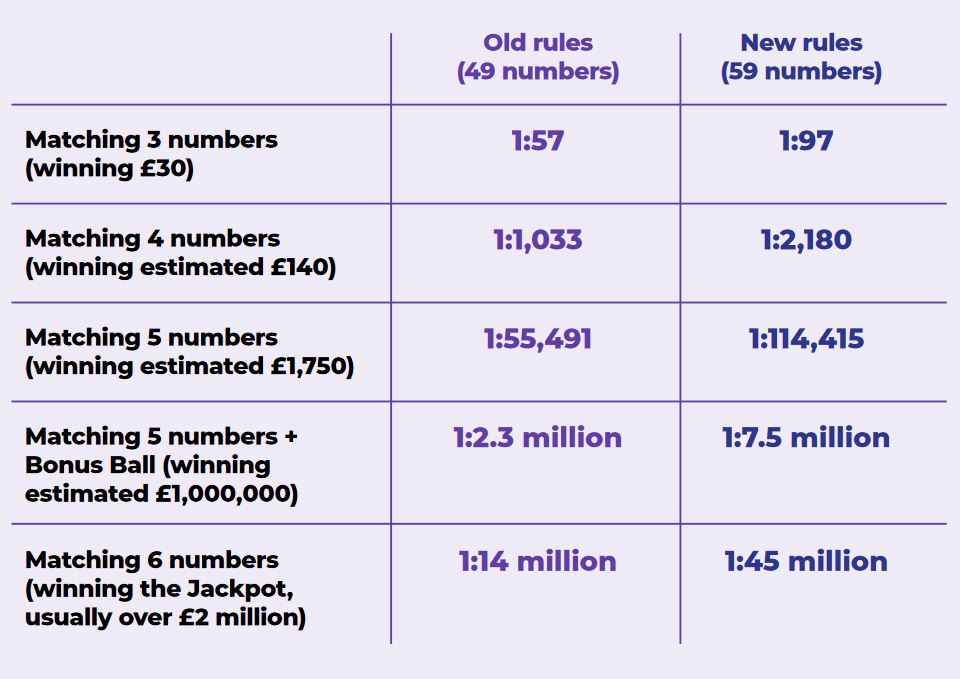
What would you do if…?
What would you
do if…?
This activity supports young people discussing how they may address concerns about gambling with their friends.
Time
10-15 Minutes
Materials to print
Picture of a target,
blue-tack
What Would You Do If: Scenario Handouts
Method
1.
Select what statements may be most
relevant for your group and how
many you want to use. Cut the
scenarios individually, fold each piece
of paper and put them all in a basket.
2.
Explain to the group that each
scenario describes a situation which
a friend might tell them about, and
that the aim of the game is to discuss
if they would be concerned about
their friend and what they could do.
You may want to discuss
confidentiality and to ask
participants to refer to friends
generically, without making names.
3.
Explain that the target represents a
gradient of risk and concern: the
bull’s eye being the highest level of
concern/risk and the outmost circle
being a level of no risk and no
concern.
4.
Ask each participant to pick a
statement from the basket.
5.
One at a time, ask a participant to
read out loud the scenario they have
on their paper, and to place it on the
target according to how concerned
they would be for a friend in those
circumstances.
6.
Ask the rest of the group to share
their views: you may want to support
them in considering the risks
involved in that scenario and the
possible consequences. Based on
the outcome of the discussion, they
may move the statement to a
different circle of the target.
7.
If the discussion highlights that the
scenario represents a situation with
some level of concern or risk, ask
them to share their thoughts on the
following three points:
why there might be a concern,
what kind of risk could the
scenario involve;
what they could say to their
friend;
who they could share their
concern with (e.g. highlight that
they should share any concern
with a parent, teacher or other
reliable adult).
8.
Move on to the next person, with a
new statement.
Alternative options:
This game can be done in pairs or in small groups. Instead of using the picture of a target, you could ask the group to stand in a circle, and to step closer or further away from the centre based on their perceived level of risk/concern for each statement.
Alternative Notes:
If a participant shares that they themselves or some-one they know is or was in one of the scenarios that they read, please make sure that at the end of the activity you follow up with a one-to-one conversation, to check if there is any cause of concern that you may need to address.
What would you do if…?
Scenario Handouts
Please feel free to write your own scenarios and/or to
choose the statements that you feel might be relevant
for your group.
You notice your friend is spending a considerable amount of time on their own, playing free online gambling games.
Your friend says that they have managed to get past the age identification on a bingo website.
Your friend says they’ve spent their pocket money on lottery tickets.
Your friend asks you if they could borrow £5 to buy a scratch card.
Your friend mentioned that they are using their parents’ credit card to pay for loot boxes on their favourite computer game.
Your friend says that they have managed to get past the age identification on a bingo website.
Your friend says they haven’t slept much because they were playing online roulette games all night.
Your friend says they play gambling-style computer games on a free roulette website because they’re bored.
Your friend often seems distracted. When you ask them what’s going on, your friend says they’re just thinking about how they can buy more loot boxes on their favourite computer game.
You notice your friend doesn’t have any money for their lunch. When you ask why, they said they used that money to buy a few scratch cards.
You discover your friend lied about having spent all their pocket money on a fruit machine.
You are talking with your friend about a computer game that you’ve both played, which contains loot boxes. You ask your friend how much money they’ve spent on opening loot boxes and they answer that they don’t know as they’ve not kept track of it and they can’t remember.
Your friend says they feel better when they gamble and encourages you to do the same if you’re feeling bored or sad.
Your friend recently turned 16 but looks a bit older. They say they’ve got a fake ID and want to try and get into the bookies.
Your friend says that they usually pick numbers for the national lottery with their parents.
Your friend wants to save money to buy a new phone, but it’s taking a long time. Another friend suggests they could use some of the savings to buy a few scratch cards as
that could help them reach the needed amount much quicker.
Your friend says that they have managed to get past the age identification on a bingo website.
Your friend decides to buy a raffle ticket for a local fundraising event.
Your friend tells you that they like playing online games because they can interact with other players on the bingo website.
Your friend says that they use £3 of their pocket money to go to the arcades once a month.
Your friend shares with you that they are worried about their sibling, whom they see playing gambling-style computer games most nights.
Your friend, who is 15 years old, tells you that they want to ask their 19-year-old sibling to buy a lottery ticket for them.
Your friend says they have bought £50 worth of loot boxes on a computer game using the card details their parents had
saved on a laptop. Your friend is now scared of their reaction if they find out, so they have been lying to the parents about
what they use the laptop for.